Best Practices Articles

Unlocking Partner Sales Potential through Co-Selling: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- What is an example of co-selling?
- What is a co-seller?
- What is the difference between cross-selling and co-selling?
- What is the difference between co-marketing and co-selling?
- What is co-selling with partners?
- What are partnership selling examples?
- What is a co-sales process?
- What are the best practices for co-selling?
- What is co-selling with AWS?
- What is co-selling with Microsoft?
Over the past several years, co-selling has become a pivotal strategy for businesses seeking to expand their reach and enhance their sales outcomes in an increasingly interconnected market. This collaborative approach enables companies to join forces, combining their unique strengths, market insights, and resources to address customer needs more effectively and efficiently than they could. Co-selling is not just about sharing leads or marketing materials; it's about creating a unified front that presents integrated solutions to the market, unlocking new opportunities, and driving mutual growth.
The essence of co-selling lies in its ability to bring together diverse entities, from multinational corporations like AWS and Microsoft to smaller specialized firms, fostering partnerships that transcend traditional competitive boundaries. By pooling resources and expertise, companies can tackle more significant market segments, innovate more rapidly, and deliver superior customer value. This strategic collaboration is particularly relevant in today's digital landscape, where integrating services and solutions can significantly enhance the customer experience and lead to higher conversion rates.
This article will delve into what co-selling entails its benefits, critical practices, and how major tech players leverage this approach to dominate global markets. We will explore real-life examples of co-selling, dissect the processes involved, and outline best practices to help businesses of all sizes implement effective co-selling strategies. Whether new to co-selling or looking to refine your existing approach, this comprehensive exploration will provide valuable insights and guidance.
1. What is an example of co-selling?
Co-selling is a collaborative sales strategy where two or more organizations partner to sell products or services jointly. This approach allows businesses to enhance market penetration, reduce operational costs, and increase sales opportunities by leveraging each other's resources, customer networks, and market presence.
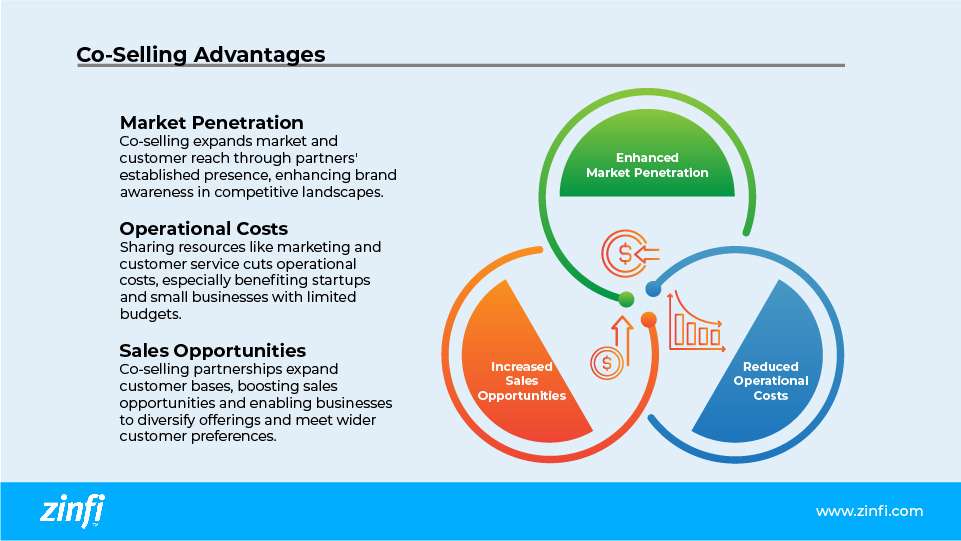
- Enhanced Market Penetration: Co-selling enables companies to access new markets and customer bases by leveraging the established market presence of their partners. This collaboration allows for a more extensive reach and brand awareness, particularly beneficial in competitive markets.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Companies can significantly reduce their operational expenses by sharing resources, such as marketing campaigns and customer service efforts. This is particularly advantageous for startups and small businesses that operate under tight budget constraints.
- Increased Sales Opportunities: Co-selling partnerships allow businesses to tap into a broader customer base, enhancing the possibility of sales that might not have been feasible independently. This approach enables companies to diversify their offerings and cater to more overall customer preferences.
Workflow automation in co-selling can streamline these processes, enhance collaboration, and enable more strategic decision-making, ultimately leading to increased efficiency and growth.
2. What is a co-seller?
A co-seller is a company or individual that partners with another business to sell complementary products or services. This collaborative relationship is built on sharing resources, information, and strategies to achieve mutual sales goals.
- Through-Channel Marketing Automation (TCMA): TCMA is critical in empowering partner ecosystems, enabling brands to manage and automate their marketing programs effectively. Co-sellers in such ecosystems can benefit from streamlined partner recruitment, onboarding, and co-marketing efforts.
- Co-Selling and Co-Marketing Strategies: Within the TCMA framework, co-selling involves joint efforts to sell complementary offerings, while co-marketing focuses on mutual promotion. Both strategies are essential for maximizing the reach and effectiveness of co-sellers.
- Enhanced Reach through TCMA: Platforms like ZINFI provide essential tools for lead management, co-branded marketing automation, and performance tracking. These features assist co-sellers in managing leads efficiently and executing co-branded marketing strategies.
3. What is the difference between cross-selling and co-selling?
Cross-selling and co-selling are both sales strategies but differ in approach and execution. Cross-selling involves suggesting additional products or services to an existing customer. At the same time, co-selling refers to the collaboration between two or more companies to sell complementary products or services to expand their customer base and market reach.
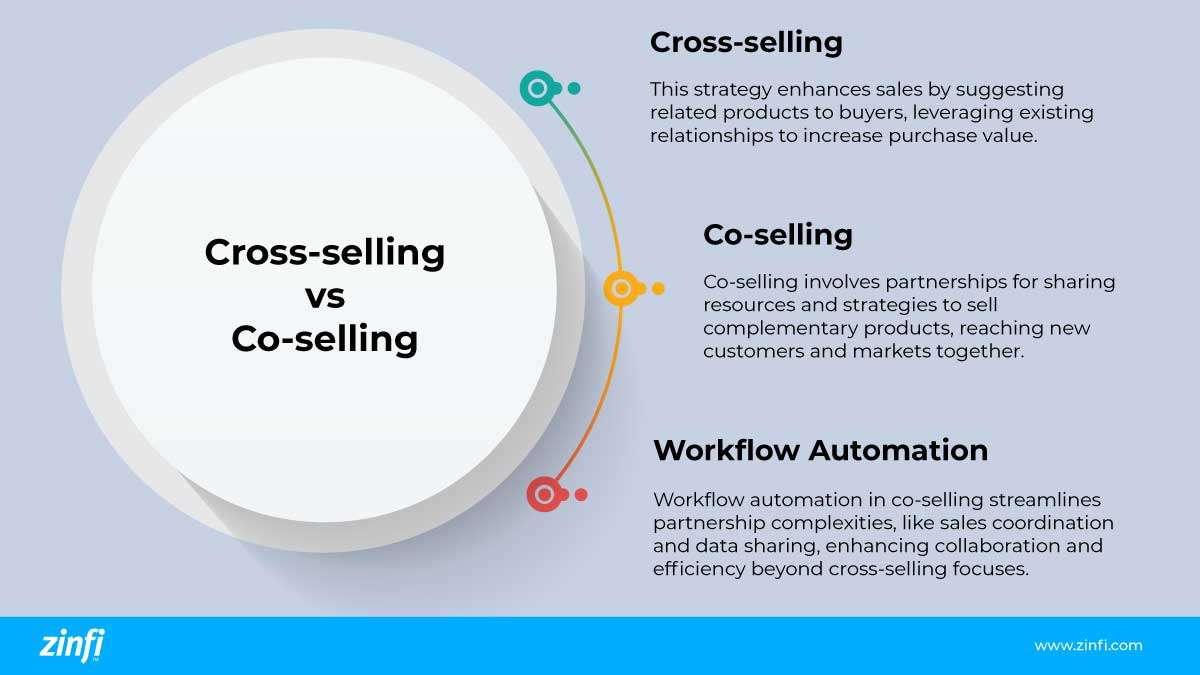
- Cross-Selling: This strategy focuses on increasing the value of a sale by recommending related products or services to customers who are already making a purchase. It relies on leveraging existing customer relationships to boost sales.
- Co-selling: Unlike cross-selling, co-selling is based on partnerships between different companies. It involves jointly sharing resources, information, and strategies to sell complementary products or services. This approach is designed to reach new customers and markets that might be inaccessible to each company individually.
- Role of Workflow Automation: In co-selling, workflow automation is vital for managing the complexities of partnerships, such as coordinating sales strategies and sharing data. Automation tools streamline these processes, enabling more efficient collaboration and decision-making, which is not typically a focus in cross-selling strategy.
These distinctions and the role of workflow automation highlight the strategic differences between cross-selling and co-selling, each serving unique business objectives and operational needs.
4. What is the difference between co-marketing and co-selling?
Co-marketing and co-selling are collaborative strategies companies use to expand their market reach and sales opportunities. However, they serve different purposes and involve distinct activities. Co-marketing focuses on joint promotional efforts, while co-selling is about directly partnering to sell products or services.
- Definition and Focus: Co-marketing is a partnership between two or more companies to market each other’s products or services jointly. The focus is combining resources to increase brand awareness, reach new customer segments, and generate leads through shared marketing campaigns. In contrast, co-selling involves two or more companies collaborating to sell products or services. Here, the focus is leveraging each partner's sales resources, networks, and customer relationships to close deals and increase revenue.
- Activities Involved: In co-marketing, joint advertising, shared content creation (such as blogs, webinars, and whitepapers), co-branded events, and shared social media campaigns. The aim is to pool marketing resources and audiences to achieve greater visibility and lead generation than either company could achieve alone. On the other hand, co-selling activities involve sales teams from each company working together, sharing customer leads, engaging in joint sales calls or presentations, and combining sales strategies to facilitate the selling process.
- Goals and Metrics: Co-marketing aims to enhance brand presence and generate leads by tapping into each other’s strengths and customer bases. Success metrics might include engagement rates, lead generation numbers, and increased traffic or inquiries. In contrast, co-selling is directly aimed at increasing sales and revenue through combined sales efforts. Metrics for co-selling success include the number of deals closed, revenue generated from joint sales efforts, and customer acquisition costs.
- Relationship Dynamics: Co-marketing relationships can be more flexible and project-based, focusing on specific campaigns or events. These partnerships can be between companies with complementary or unrelated products and services. Co-selling relationships are often more profound and strategic, requiring alignment in sales processes, product integration, and customer service. These partnerships are typically formed between companies with complementary offerings that can be sold as a package or bundled solution.

By understanding the differences between co-marketing and co-selling, businesses can better strategize their partnership efforts to maximize brand exposure and revenue generation.
5. What is co-selling with partners?
Co-selling with partners involves two or more businesses collaborating to sell their products or services. This strategy leverages all partners' combined strengths, customer bases, and sales resources to drive sales and expand market reach.
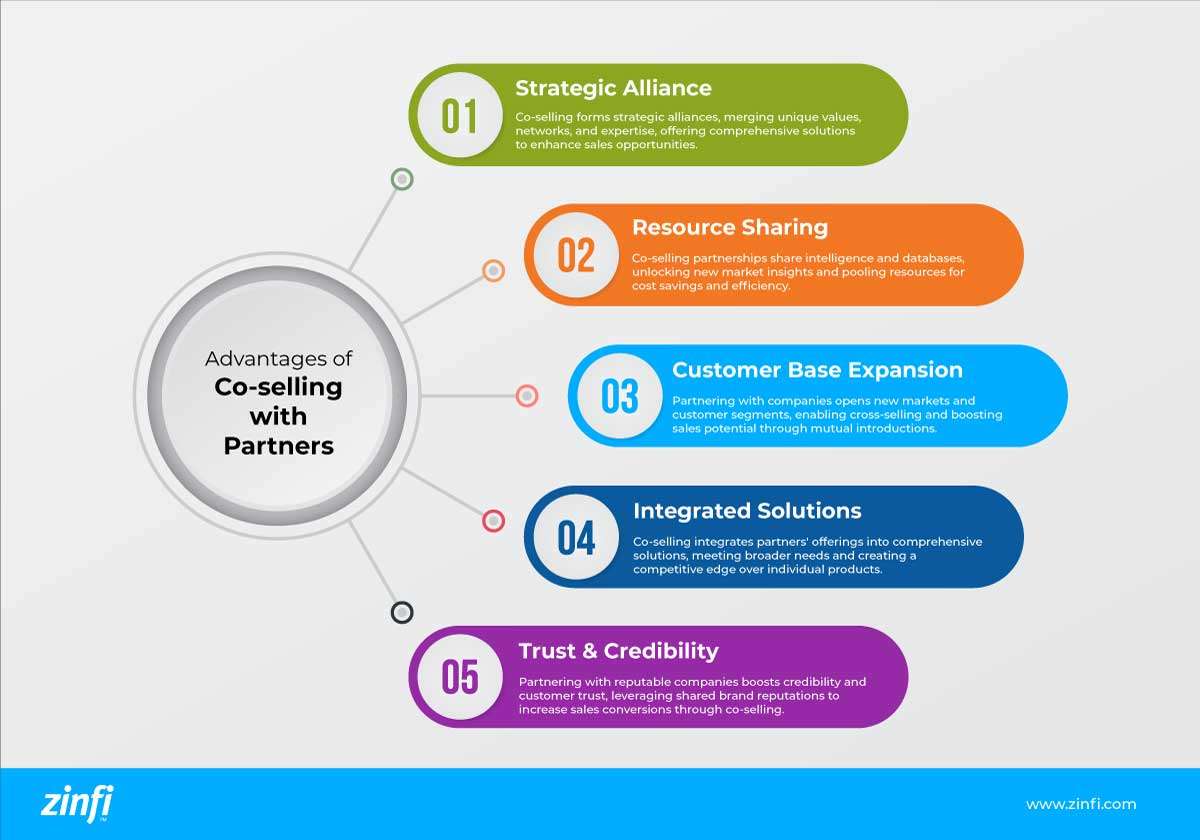
- Strategic Alliance: Co-selling with partners creates a strategic alliance where each party brings unique value propositions, customer networks, and market expertise. This collaborative effort allows partners to offer more comprehensive solutions to their customers, enhancing the value provided and increasing the chances of closing sales.
- Resource Sharing: In a co-selling partnership, companies share sales intelligence, market research, and customer databases. This sharing enables each partner to gain insights into new market segments, and customer needs that they might need access to independently. It also allows for pooling resources in sales efforts, leading to cost savings and increased efficiency.
- Customer Base Expansion: By partnering with other companies, businesses can access new customer segments and markets that were previously out of reach. Each partner can introduce the other to their existing customers, leading to cross-selling opportunities and increased sales potential.
- Integrated Solutions: Co-selling often involves integrating the partners’ products or services to create comprehensive solutions that meet broader customer needs. This integration can lead to a competitive advantage, as the combined offering is often more appealing than individual products or services.
- Trust and Credibility: Partnering with established and respected companies can enhance a business's credibility and trustworthiness in the eyes of potential customers. When companies co-sell, they leverage each other's brand reputations, leading to increased customer confidence and higher sales conversion rates.
In summary, co-selling with partners is a mutually beneficial strategy leading to increased sales, expanded market reach, and stronger customer relationships.
6. What are partnership selling examples?
Partnership selling refers to two or more companies collaborating to sell complementary products or services. This approach can take various forms, from formal alliances and joint ventures to more informal referral agreements.

- Technology Integrations: A typical example of partnership selling is in the technology sector, where software companies form alliances to offer integrated solutions. For instance, a CRM software provider might partner with an email marketing platform to provide a comprehensive customer engagement suite.
- Financial Services: In the financial services industry, banks often partner with insurance companies to offer bundled banking and insurance services to their customers. This can include home loans with integrated home insurance or savings accounts with life insurance policies.
- Retail Collaborations: Retailers often engage in partnerships selling special promotions or co-branded products. For example, a fitness wear brand might partner with a health food company to offer customers a package deal that combines both products, appealing to a shared target audience interested in health and wellness.
- Service Sector Alliances: Service providers such as travel agencies, hotels, and airlines often engage in partnership selling. A travel agency may partner with hotels and airlines to offer a complete vacation package, providing customers with a seamless travel experience while benefiting from shared marketing and sales efforts.
- Automotive Industry Partnerships: In the automotive industry, car manufacturers may partner with finance companies to offer customers attractive financing options when purchasing a new vehicle. This partnership helps facilitate the sales process for the car manufacturer while providing the finance company with new customers.
- Cross-Industry Bundles: Companies from different industries sometimes come together to create unique bundled offerings. For example, a telecommunications company might partner with a streaming service to offer a bundle that includes both internet service and a streaming subscription at a discounted rate.
These examples demonstrate the variety of ways companies can engage in partnership selling to enhance their product offerings, reach new customers, and increase sales. By leveraging each partner's strengths and customer bases, businesses can create synergistic relationships that benefit all parties involved.
7. What is a co-sales process?
The co-sales process involves partners collaborating throughout the sales cycle to leverage each other's resources, strengths, and market presence to close deals more effectively. This process typically includes joint planning, lead sharing, co-branded marketing efforts, and combined sales meetings.
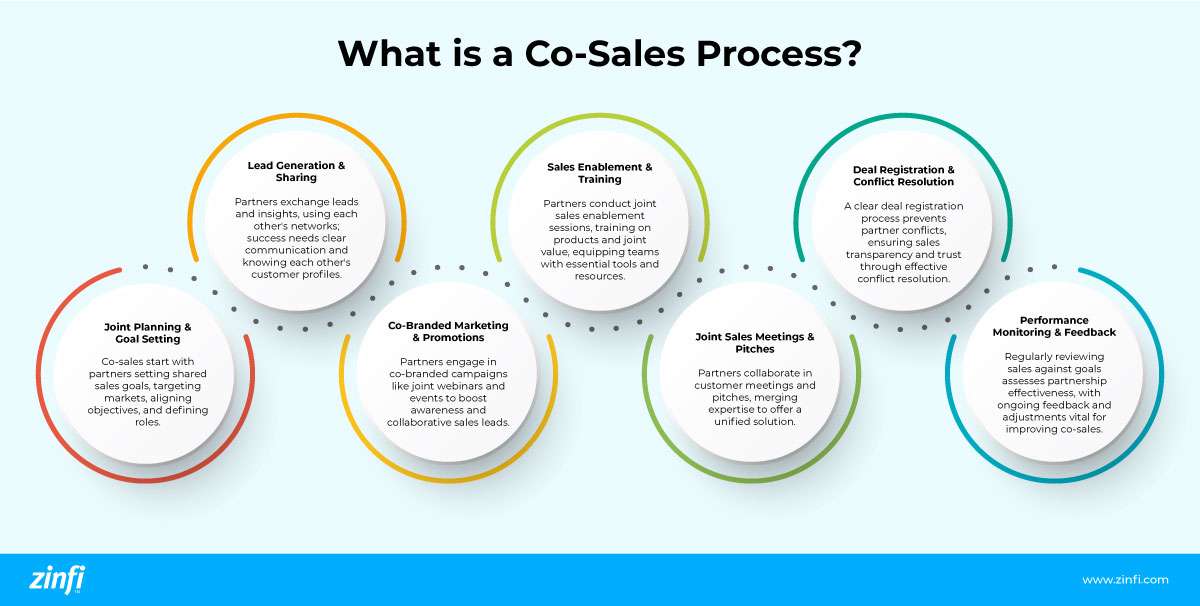
- Joint Planning and Goal Setting: The co-sales process begins with partners collaborating to set common sales targets and strategies. This involves identifying target markets, aligning sales objectives, and defining roles and responsibilities.
- Lead Generation and Sharing: Partners share leads and market intelligence, leveraging each other's customer networks and insights. Effective lead sharing requires clear communication and understanding of each partner's ideal customer profile.
- Co-Branded Marketing and Promotions: Partners may use co-branded marketing campaigns to generate awareness and leads. This can include joint webinars, shared content marketing, and co-hosted events to drive collaborative sales opportunities.
- Sales Enablement and Training: To ensure success in the co-sales process, partners often engage in joint sales enablement sessions. This can involve training on each other’s products or services, understanding the joint value proposition, and equipping sales teams with the necessary tools and resources.
- Joint Sales Meetings and Pitches: Partners may join in customer meetings and pitches, combining their expertise and resources to present a unified solution to the customer.
- Deal Registration and Conflict Resolution: A straightforward deal registration process helps avoid conflicts between partners and ensures transparency in the sales process. Effective conflict resolution mechanisms are also essential to maintain trust and collaboration.
- Performance Monitoring and Feedback: Regular reviews of the sales performance against the set goals help understand the partnership's effectiveness. Continuous feedback and adjustments are crucial for improving the co-sales process and outcomes.
The co-sales process is about leveraging the strengths of each partner to achieve better sales results than either could achieve independently. It requires clear communication, shared goals, and mutual respect between partners.
8. What are the best practices for co-selling?
Best practices for co-selling include clear communication, setting mutual goals, regular training and enablement, transparent lead management, and maintaining a customer-centric approach. These practices help ensure the partnership is productive and beneficial for all parties involved.

- Establish Clear Communication Channels: Regular and clear communication is essential for coordinating sales efforts, sharing information, and resolving issues promptly.
- Define Mutual Goals and Objectives: Partners should agree on shared sales targets, market strategies, and key performance indicators to ensure aligned efforts.
- Engage in Regular Training and Enablement: Continuous training ensures that all sales teams are well-versed in each other’s products, services, and sales strategies, enhancing their ability to sell together effectively.
- Implement Transparent Lead Management Processes: A straightforward process for sharing, tracking, and following up on leads is crucial to prevent conflicts and ensure that both parties contribute to the partnership.
- Maintain a Customer-Centric Approach: Always prioritize the customer’s needs and ensure the partnership delivers real value to the end customer.
- Leverage Co-Branding Opportunities: Utilize co-branded materials and campaigns to present a unified front to customers and leverage each other's brand strengths.
- Regularly Review and Adjust Strategies: Regular reviews of the partnership’s performance against goals allow for timely adjustments and continuous improvement.
- Celebrate Joint Successes: Recognizing and celebrating wins can help boost morale and reinforce the value of the partnership.
Following these best practices can help ensure that co-selling efforts are successful, leading to increased sales, expanded market reach, and a strengthened partnership.
9. What is co-selling with AWS?
Co-selling with AWS refers to the collaboration between Amazon Web Services (AWS) and its partners to sell services and solutions jointly. This involves leveraging AWS’s extensive network, resources, and marketplace to enhance sales opportunities for AWS and its partners.
- AWS Partner Network (APN): Companies that join the APN can access various resources, training, and support to build, market, and sell their AWS-based solutions.
- Marketplace Integration: Partners can list their products or services on the AWS Marketplace, making them easily accessible to a wide range of AWS customers.
- Joint Sales Engagements: AWS and its partners may engage in standard sales calls, presentations, and efforts to provide comprehensive solutions to customers.
- Access to AWS Promotions and Programs: Partners can benefit from AWS promotional programs, incentives, and discounts to facilitate co-selling efforts.
- Training and Certification: AWS provides training and certification programs to ensure that partners have the knowledge and skills to sell AWS solutions effectively.
 Co-selling with AWS allows partners to leverage the tech giant’s brand, reach, and credibility to boost their sales and market presence.
Co-selling with AWS allows partners to leverage the tech giant’s brand, reach, and credibility to boost their sales and market presence.10. What is co-selling with Microsoft?
Co-selling with Microsoft involves partnering with the tech giant to sell combined solutions incorporating Microsoft's products, such as Azure, Microsoft 365, and Dynamics 365. This partnership aims to provide comprehensive solutions to meet customer needs more effectively.
- Microsoft Partner Network (MPN): Joining the MPN provides businesses with resources, training, and support to develop, market, and sell their solutions built on or integrated with Microsoft products.
- Go-To-Market Services: Microsoft offers go-to-market support to help partners market their solutions, including co-marketing opportunities, sales enablement content, and joint customer outreach.
- Co-Sell Ready Program: Microsoft’s Co-Sell Ready program allows partners to collaborate with Microsoft’s sales teams worldwide, offering joint sales opportunities, shared leads, and co-selling experiences to reach more customers.
- Sales Enablement and Training: Microsoft provides extensive training and certifications for partners to ensure they have the expertise to effectively sell Microsoft products and solutions.
- Marketplace Presence: Partners can list their solutions on Microsoft AppSource and Azure Marketplace, increasing visibility among potential customers and making it easier for them to purchase solutions.
- Incentives and Rewards: Microsoft offers various incentives to encourage and support co-selling activities with partners, including financial benefits and rewards.
Co-selling with Microsoft allows partners to leverage Microsoft’s vast network, brand, and resources to enhance their own sales efforts and expand their reach in the market. This collaboration is designed to deliver integrated solutions that address the complex needs of modern businesses and drive mutual growth for Microsoft and its partners.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, co-selling has emerged as a fundamental strategy for businesses aiming to thrive in today's competitive landscape. Companies can leverage combined strengths by fostering collaborative partnerships to create more compelling and comprehensive market offerings. The journey through various facets of co-selling, from understanding its core principles to applying best practices and navigating successful partnerships with giants like AWS and Microsoft, underscores the transformative power of collaboration.
Implementing co-selling strategies requires careful planning, alignment of goals, and commitment to mutual success. As highlighted, the essence of effective co-selling lies in transparent communication, shared objectives, and an unwavering focus on delivering customer value. The success stories of co-selling with AWS and Microsoft provide a blueprint for how businesses can scale their operations and achieve unprecedented growth through strategic alliances.
As we look ahead, the role of co-selling in achieving business success is expected to grow even more significant. The ability to adapt to evolving market demands and the readiness to collaborate and innovate will set apart the leaders from the followers. For businesses ready to embark on this collaborative journey, the future holds limitless possibilities for growth, innovation, and customer satisfaction. Embracing co-selling is not merely a tactical move—it's a strategic imperative for sustainable development and market leadership in the digital age.
Read our article on how to Accelerate Revenue at a Lower Cost by Automating Partner-Driven Co-Selling.
Note: All product names, logos, and brands used in this article are properties of their respective owners. All company, product, and service names used in this article are for identification purposes only. Use of these names, logos, and brands does not imply endorsement.
For more information, please check this article.


Best Practices Guidebook
 How to Start and Scale Partner Ecosystems Best Practices
How to Start and Scale Partner Ecosystems Best PracticesDownload Guide
 The Evolution of PartnerOps: Past, Present & Future Best Practices
The Evolution of PartnerOps: Past, Present & Future Best PracticesDownload Guide
 Mastering Channel Sales: Strategies, Best Practices, and Growth Tactics for 2025
Mastering Channel Sales: Strategies, Best Practices, and Growth Tactics for 2025Download Guide
 Winning with Partner Advisory Councils: Best Practices for Partner Engagement & Growth
Winning with Partner Advisory Councils: Best Practices for Partner Engagement & GrowthDownload Guide
 The Future of Partner Ecosystems Best Practices
The Future of Partner Ecosystems Best PracticesDownload Guide
 The AI Revolution: How Technology and Talent are Shaping the Future
The AI Revolution: How Technology and Talent are Shaping the FutureDownload Guide
 Top 105 Partner Management Metrics that Matter Best Practices
Top 105 Partner Management Metrics that Matter Best PracticesDownload Guide
 Mastering PRM Integration Best Practices
Mastering PRM Integration Best PracticesDownload Guide
 Building a Sales Partner Portal with Salesforce Best Practices
Building a Sales Partner Portal with Salesforce Best PracticesDownload Guide
 Building and Managing Partner Ecosystems Best Practices
Building and Managing Partner Ecosystems Best PracticesDownload Guide
 Mastering Co-Marketing and Co-Selling Best Practices
Mastering Co-Marketing and Co-Selling Best PracticesDownload Guide
 Transforming Partner Ecosystems Best Practices
Transforming Partner Ecosystems Best PracticesDownload Guide
 Mastering Partner Ecosystems Best Practices
Mastering Partner Ecosystems Best PracticesDownload Guide
 Mastering Partner Onboarding Best Practices
Mastering Partner Onboarding Best PracticesDownload Guide
 Partner Ecosystem Management Best Practices
Partner Ecosystem Management Best PracticesDownload Guide
 B2B Marketing in the Age of Intelligence Best Practices
B2B Marketing in the Age of Intelligence Best PracticesDownload Guide
 Multi-Partner Co-Selling Best Practices
Multi-Partner Co-Selling Best PracticesDownload Guide
 A Guide to Enhance Channel Sales Efficiency
A Guide to Enhance Channel Sales EfficiencyDownload Guide







